Cloud Security: Safeguarding Your Data in the Digital Sky
Security is of highest priority in the significant field of cloud computing, as data travels over the digital sky. Strong security measures must be put in place as more and more people and organizations trust the cloud with their sensitive data in order to protect themselves against attacks and hacking attempts. We’ll go further into the topic of cloud security in this blog, breaking down its best practices, obstacles, and ideas into understandable language.
Understanding Cloud Security
A set of processes, tools, and guidelines referred to as cloud security are used to protect information, programs, and hardware in cloud environments. Building a digital palace in the clouds to protect data from breaches, hacks, and unwanted access is similar to doing so. Cloud security includes multiple security layers, such as network security, identity management, access controls, and encryption, to guarantee the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of information stored in the cloud.
Common Threats and Challenges
Even with its many advantages, cloud computing has drawbacks. Cloud security is frequently threatened by malware, scams, insider threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Sensitive data may be compromised, company activities may be interfered with, and trust and reputation may be harmed. Furthermore, there are particular difficulties in managing security in multi-cloud and hybrid cloud setups, including complexity, visibility, and compliance.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
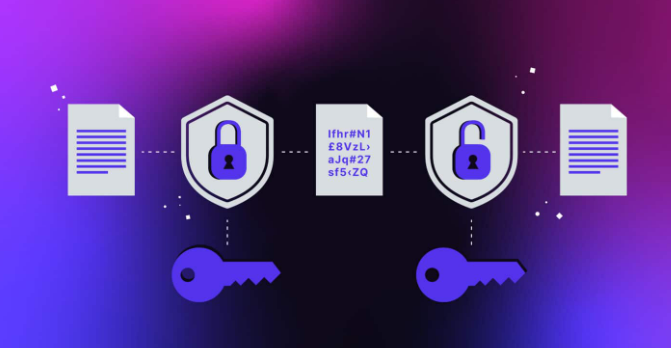
Encryption: To guard against unwanted access and data breaches, data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Use strong encryption techniques and key management procedures to guarantee the privacy and accuracy of cloud data.
Access Controls: Strong access controls and authentication procedures should be put in place to confirm user identities and limit access to resources and data that are sensitive. To enforce access regulations and stop unwanted access, use least privilege principles, role-based access control (RBAC), and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
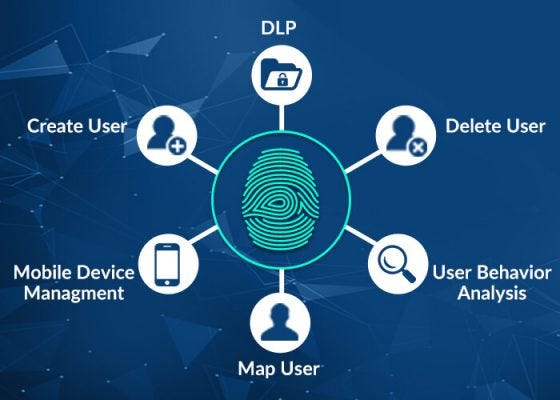
Identity Management: To control user identities, permissions, and authentication methods across cloud services and apps, employ centralized identity management systems. By doing this, it is made sure that only individuals with permission can access cloud services and data.
Network Security: To monitor and secure network traffic in the cloud, put in place network security controls like firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and virtual private networks (VPNs). To identify and address security risks, split networks, encrypt data, and keep an eye on network behavior.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response: To identify and address safety problems quickly, set up continuous security monitoring and tracking. Create emergency response plans and processes to lessen the effects of security breaches and quickly resume regular operations.
Comments
Post a Comment